D-Orbital Geometry – Part 3
The 3rd set of D-orbitals are the last to form stable elements. The geometric explanation revels a 6D structure which terminates at the end of the Metatron’s Cube.
The 3rd set of D-orbitals are the last to form stable elements. The geometric explanation revels a 6D structure which terminates at the end of the Metatron’s Cube.
D-orbitals form cross shapes lobes that unify on the x, y, and z axis to produce a hypercubic model of the electron cloud
The 2nd set of D-orbitals contain various anomalies that are explained by the Geometric model of the atom. Part 2 of 3.

P-orbitals form in sets of 6 producing an octahedral structure. By producing this form based on the average radii for each set, we can approximate the radius for almost all elements on the periodic table.
S-orbitals form the only set of elements occupying a spherical shell. Whilst quantum theory suggests it is ‘only applicable’ to these types of atom, investigation of the atomic radius shows a discrepancy of over 100% for some elements.
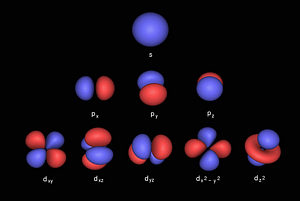
The 4 types of electron orbital can be mapped to 2D geometry, called the Seed/Flower of Life. This produces a simple geometric pattern that decodes the electron configuration.

The electron cloud is normally thought about in terms of the probability of the particle. However, our notion of a 4D Aether dispenses with this notion, returning a sense of normally to atomic physics.

The foundations of reality are defined by the atom, from which all mater is produced. These vary in radius, which can be mapped to a geometric symbol called the Seed of Life.

Geo-Nuclear physics is the application of simple polyhedra to the structure of the atomic nucleus, and consider the isotope distribution of each type of atom.

Atomic geometry is the world’s first comprehensive geometric model of the atom, that visualises the electron cloud through three-dimensional polyhedra.