What is the Cosmic Microwave Background?
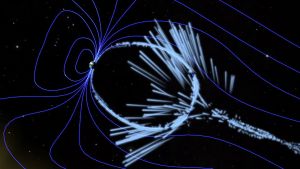
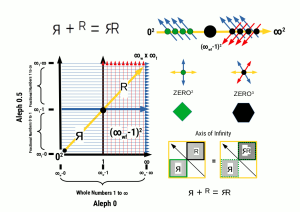
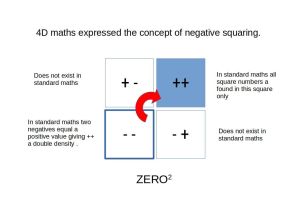
The Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation discovered in 1964 is ascribed to the remnants of the Big Bang. Yet, correlations to the atom suggest it is it more likely the energy in the vacuum, the Aether field, which undermines the notion of a photon of light.